Introduction
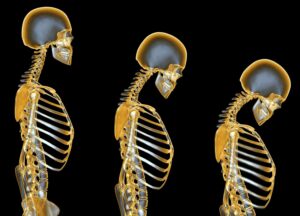
At the age of 30 and up, men and women will see a gradual change on their height and gait (walking). As individuals age, it’s typical to experience a gradual decrease in height, averaging around half an inch every decade from their peak stature. Height loss becomes more noticeable, particularly after reaching the age of 70, marking a natural aspect of the aging process.
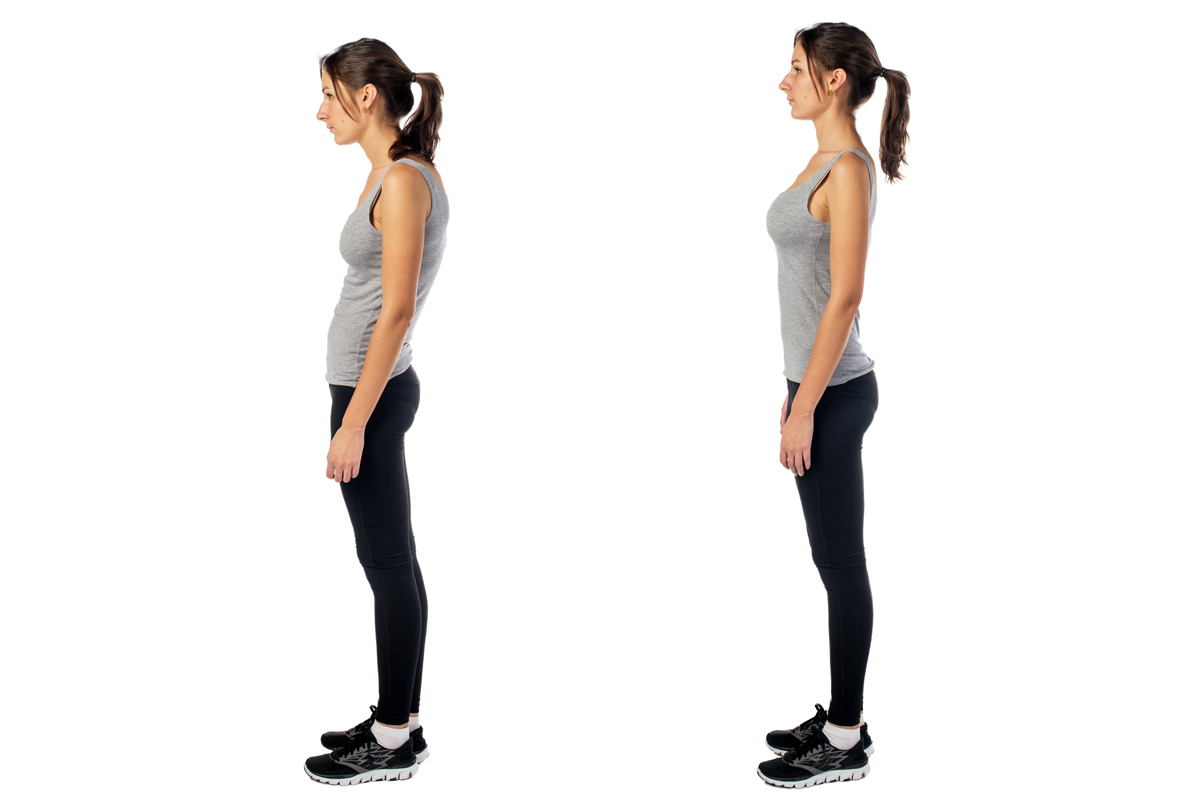
Osteopenia and osteoporosis are a medical term of decrease in bone density, ranging from mild to severe. This reduction results from calcium loss in the bones, which typically starts in women during menopause and in men around the age of 65. Additionally, there may be a slight reduction in the size of less dense bones in the spine, potentially impacting posture.
If you’re an adult living the life or a person gradually see the change in your posture, worry no more as we can give you tips and some exercise to improve or avoid bad posture.
Common Causes of Bad Posture
*Overweight
*Lack of Muscle Tone
*Extended periods of sitting
*Poor Form When Walking or Exercising
*Extended usage of electronic devices will cause neck problems and posture
*Sleeping or resting in an incorrect position.
These are some of the common habits that causes bad posture. In order to avoid these, here are some exercise to improve your posture!
Exercise
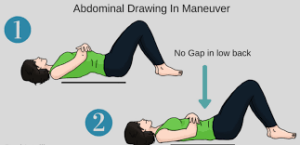
Plank
The Plank Pose helps make your posture better by making the muscles in your shoulders, back, core, buttocks, and legs stronger. It also makes sure your spine is in the right position.
How to plank:
*Lower yourself onto your hands and knees. Ensure your hands are aligned with your shoulders and your knees are aligned with your hips.
*Raise onto the balls of your feet by lifting your heels and straightening your legs, forming a straight line with your body.
*Maintain an open chest and keep your shoulders pulled back.
*Hold this position for 30 to 60 seconds.
Shoulder Blade Squeeze
Shoulder blade squeezes make your posture better by making the muscles in your upper back stronger and keeping your body in the right position. They help fix rounded shoulders, which can cause pain and discomfort.
How to shoulder blade squeeze
*To do a shoulder blade squeeze, sit or stand with your back straight.
*Gently bring your shoulder blades together, squeezing them while ensuring your shoulders remain down.
*Maintain this position for a few seconds, then relax.
*Repeat to enhance posture and strengthen the upper back.
Chest stretch
Stretching your chest activates the chest muscles, stimulates blood flow, and can increase your short-term range of motion and flexibility.
How to chest stretch
*Stand tall with your feet shoulder-width apart.
*With both hands, reach behind your body and clasp your fingers together, palms facing upward.
*Maintain a straight back and arms as you gently pull your shoulders back and downward. Hold this position briefly, then release.
Cobra pose
This yoga posture expands the chest, stretches the hip flexors, and enhances spinal flexibility, while also fortifying the muscles in the arms and back.
How to cobra pose
*Lie facedown with your legs separated at hip-width.
*Bend your elbows and place them near your ribs with your palms on the floor.
*Curve your elbows and position them close to your ribs, with your palms resting on the floor.
*Gradually rise onto your forearms, elevating your chest from the floor while ensuring your hips and pelvis remain grounded.
*In a low cobra, maintain support on your forearms. In a full cobra, extend your arms fully by pressing up from the floor.
*Hold for three to six breaths.
*Repeat the cobra pose three to five times.
Chin tucks
Chin tucks assist in correcting a forward-head posture by addressing muscle imbalances. They reinforce the neck flexors and other muscles responsible for pulling the neck backward, while also stretching tense muscles along the sides of the neck.
How to chin tucks
*Maintain a straight back and upright posture, whether sitting or standing, with your shoulders pulled back.
*Use your index finger to touch your chin as a visual guide, and maintain its position throughout the exercise.
*Draw your chin directly backward, sensing a stretch along the rear of your neck.
*Hold for 5 seconds.
*Return your chin to its starting position, ensuring it touches your finger once more.
*Do 10 to 12 chin tucks.
Bird Dog
The bird dog exercise fortifies your core, crucial for maintaining good posture, while engaging your posterior muscles such as the lower back, glutes, spinal extensors, and hips.
How to bird dog
*Begin in a tabletop position, aligning your wrists under your shoulders and your knees under your hips.
*Lift your right arm forward as you simultaneously extend your left leg backward. Hold for a few seconds before returning to the initial position.
*Extend your left arm forward while simultaneously extending your right leg backward. Hold this position for a few seconds before returning to the starting position.
*Continue switching sides, raising your opposite arm and leg five times on each side.
*Perform the bird dog exercise for two to three sets.
The Bottom Line
Changes in posture are inevitable as we age, proactive measures can be taken to delay or mitigate these effects. By prioritizing activities that promote bone, joint, and muscle health, such as regular exercise, proper nutrition, and maintaining an active lifestyle, we can enhance our overall well-being and preserve our posture for longer. Embracing healthy aging practices empowers us to live life to the fullest while gracefully navigating the natural changes that come with advancing years.

 888-616-4156
888-616-4156